The 2024 Doctor’s Handbook to Patient Data Compliance Across the US
Healthcare is becoming increasingly data-driven, revolutionizing how we diagnose, treat, and prevent illnesses. While data helps streamline these processes, it also introduces a new responsibility about patient data compliance. Doctors must now not only take care of their patients’ health but also ensure the security and privacy of their patients’ healthcare data.
This can be frustrating, as it opens up many challenges on how to properly secure patient data and how long it should be legally kept. Thankfully, regulatory bodies such as HIPAA and the HITECH Act have established clear guidelines for protecting patient data.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of data privacy, the cyber threats facing healthcare, and the specifics of data compliance and state regulations.
We’ll also provide practical steps to protect your patients’ healthcare data using cloud storage solutions. This is a must-read guide you’ll want to bookmark for future referencep

Why is Patient Data Compliance So Important in Healthcare?
Because health information contains extremely sensitive information (such as a patient’s medical history), data privacy is a critical concern for health organizations.
Data privacy in the healthcare business refers to how to effectively handle, preserve, process, and exchange personal patient information such as medical records, treatment plans, and insurance information.
• Data privacy in healthcare has a variety of issues. Mainly, it is about protecting patients’ privacy and maintaining their trust in health care professionals.
• Patients dislike sharing their secrets, even with physicians, since they believe in confidentiality.
• Breaking this trust causes a loss of patient confidence, which can be detrimental not only to one physician but also to the entire healthcare system.
• Data privacy must be protected in order to comply with legal and ethical standards. Several laws govern patient data protection in the United States, notably HIPAA, with similar systems across the world.
• Employers have to comply with these requirements without fail. Failure to comply with any of these rules might result in severe penalties.
• Patient data should be protected from illegal access, theft, and alteration using cyberspace security protocols.
• An attack endangers the patient’s financial security by jeopardizing their ability to secure future healthcare coverage. Also, it has the potential to lead to identity theft and, as a result, patient fraud.
Increasing Cyberattacks that Target Electronic Health Record Data
Healthcare data continues to be a popular target for cyberattacks due to its high value on the black market. Unfortunately, as the price of patient information grows, the sector has seen an increase in data breaches. Over the previous five years, more than 90 percent of healthcare data breaches have been triggered by hacking attacks.
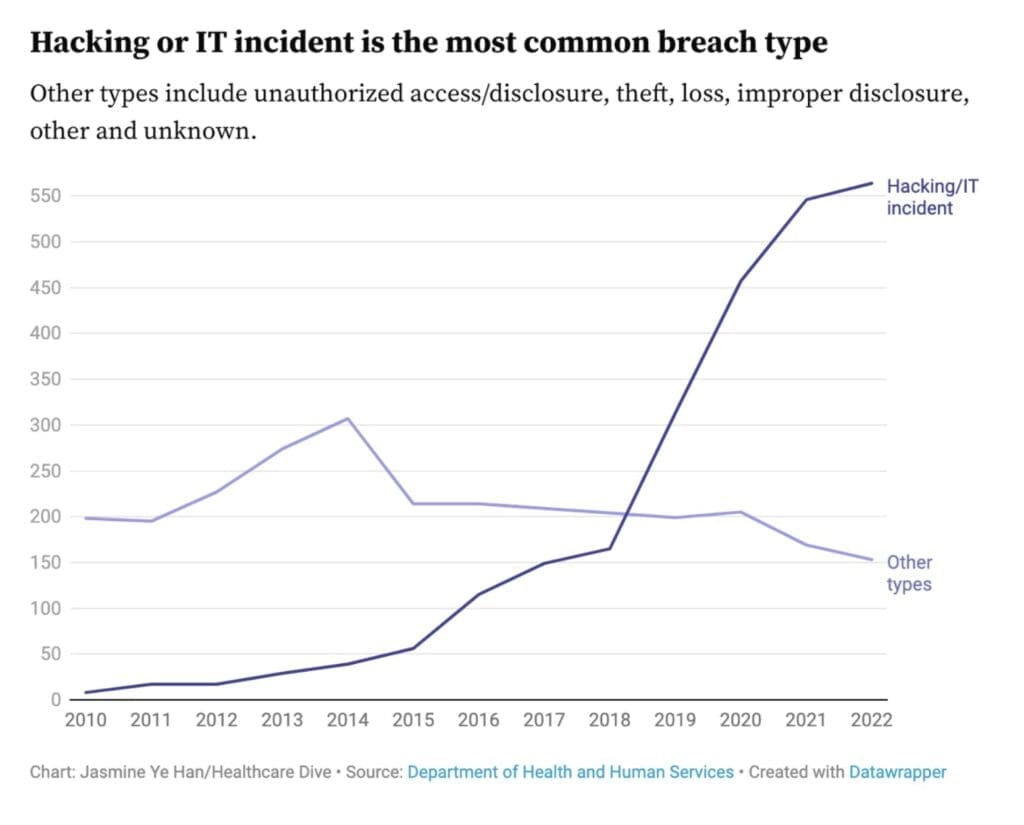
Image source: Healthcare Dive
Doctor’s can no longer afford to overlook such instances, since each healthcare data breach costs more than $10 million on average. As the frequency and complexity of data breaches grow, healthcare organizations must become more safe and robust than ever before.
In a recent report on internet crime released by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the healthcare industry emerged as the most heavily targeted sector for cyberattacks. These attacks not only jeopardize patient safety but also constitute a significant national security threat.
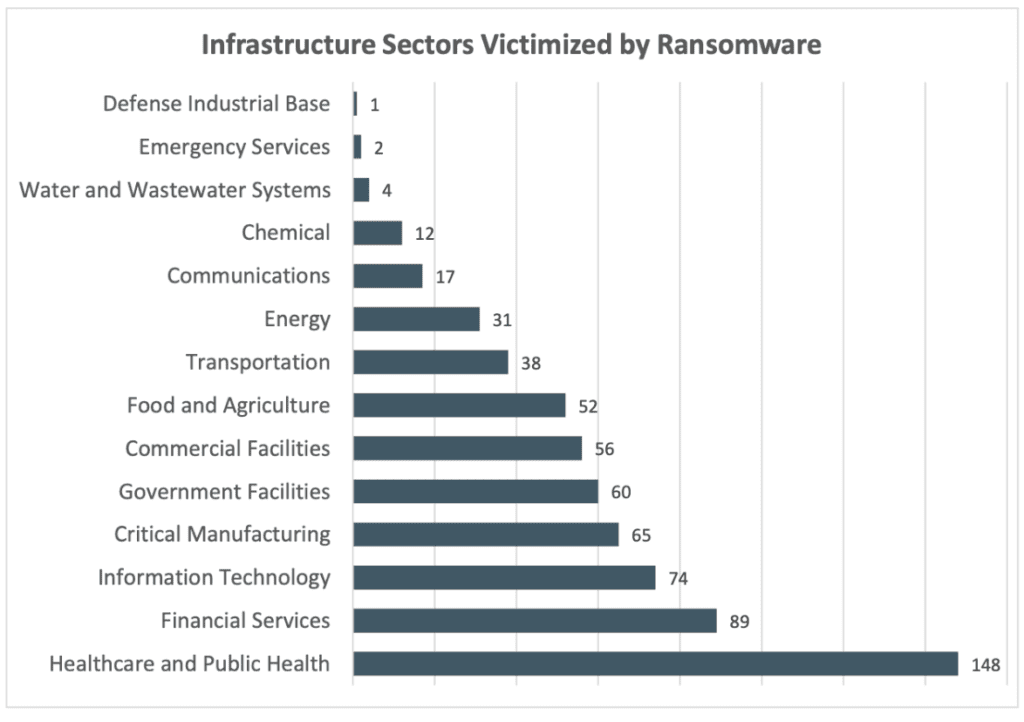
Image source: FBI Internet Crime Report 2021
Patient Data Compliance Regulations to Follow
Before we go deeper into data compliance in healthcare, we first need to know what it exactly means. Data compliance refers to the process of planning, storing, organizing, and managing healthcare data. Healthcare organizations prioritize compliance to protect safety and avoid costly cases of fraud and abuse.
These are the main regulatory frameworks healthcare practices need to follow when managing patients’ digital assets. Ignoring these rules can lead to significant fines.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is a US law that was signed into action in 1996 to protect sensitive patient information. More than two decades later, the law continues to be the most essential piece of legislation protecting patient data in the United States.
Electronic health record companies and other software companies need to align with HIPAA’s standards to avoid penalties and serious legal action.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH)
HITECH became law in 2009 as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, thanks to Congress.
The act seeks to promote health information technology throughout the country. Additionally, HITECH enhanced the penalty for HIPAA privacy and security violations. Penalties often vary between $100 and $50,000 per occurrence. HITECH also imposes a maximum penalty of $1.5 million.
Compliance Alone Won’t Protect Your Healthcare Data from Cyberattacks
Every year, the healthcare industry experiences a surge in data breaches. But why?
Mandatory compliance laws like HIPAA provide a framework for improving both data privacy and security. However, these restrictions are not powerful enough to address contemporary hacking dangers.
For example, HIPAA does not require an initial certification from a third-party security assessor. As a result, EHR companies frequently identify weaknesses in their data operations only after a hack or data breach occurs.
Wondering how healthcare providers can avoid hefty fines? Here’s how: Archie, a handy add-on for your current EHR system, can seamlessly archive and backup all your data on a secure cloud server. So, even if your EHR provider falls victim to a cyberattack, your patients’ data remains safe and sound, tucked away in a secure digital vault.
Counting solely on HIPAA guidelines won’t cut it. Ensure you’re safeguarding your patient’s data by using archival software like Archie. It’s your ticket to staying ten steps ahead in the game.
These are the main regulatory frameworks healthcare practices need to follow when managing patients’ digital assets. Ignoring these rules can lead to significant fines.
How Long Should Doctor’s Keep Patient Healthcare Data?
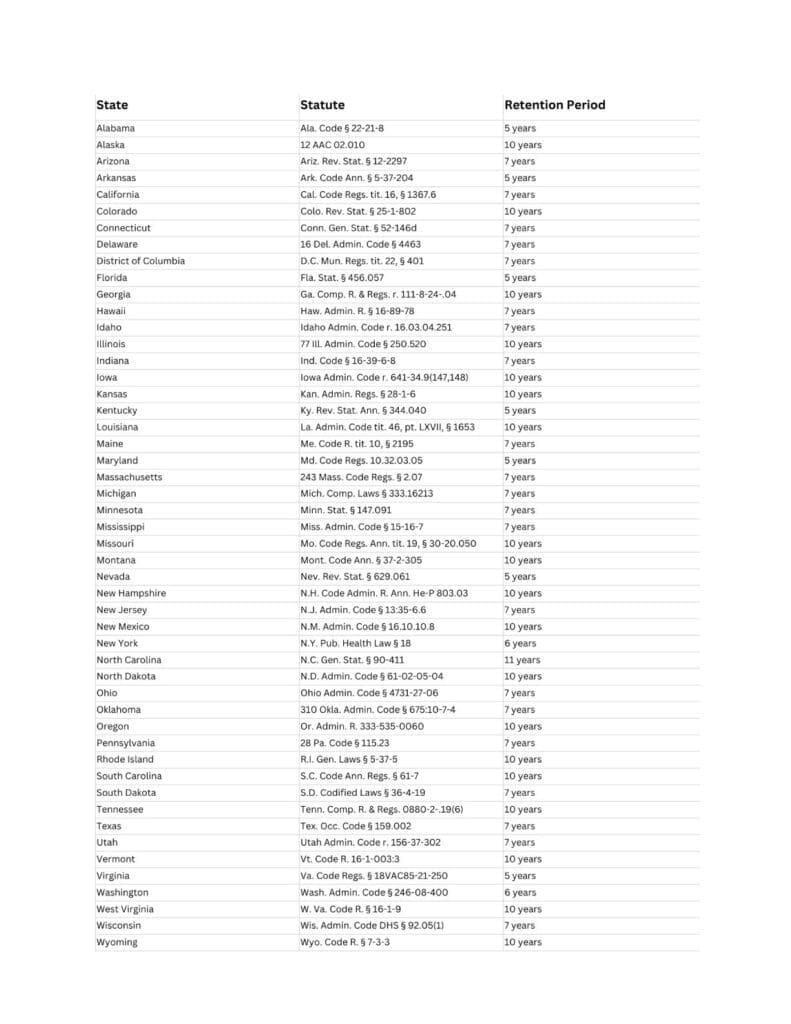
Part of staying compliant with data regulations is knowing how long healthcare providers are legally required to hold onto their patients’ data.
Each state has its own rules for how long patient records must be retained. Some states require providers to keep information for as few as three years, while others demand retention periods of 10 years or more. The retention period only begins on the date of the final treatment.
Here’s a table for retention policies by state:
Conclusion
Securing patient data compliance in the US healthcare system isn’t an easy task. As the healthcare industry becomes more data-driven, securing patient information becomes increasingly vital. While regulations like HIPAA and the HITECH Act give guidance, they are simply not enough to fight emerging cyber dangers.
With an increase in cyberattacks aimed at EHR companies, healthcare providers need to take extra measures to protect their patients’ data. With live data-backup and storage with Archie, doctor’s can now get the extra layer of protection they need without relying solely on their EHR provider.
Our latest Blog & News


